|
JKQTPlotter trunk/v5.0.0
an extensive Qt5+Qt6 Plotter framework (including a feature-richt plotter widget, a speed-optimized, but limited variant and a LaTeX equation renderer!), written fully in C/C++ and without external dependencies
|
 |
JKQTPlotter trunk/v5.0.0
an extensive Qt5+Qt6 Plotter framework (including a feature-richt plotter widget, a speed-optimized, but limited variant and a LaTeX equation renderer!), written fully in C/C++ and without external dependencies
|
This project (see ./examples/multiplot/) shows how several JKQTPlotter widgets can be combined to in a layout (based on the Qt layouting system). It also shows how axes in such a layout can be linked to improve user experience.
The source code of the main application can be found in test_multiplot.cpp.
First three plots are generated and put into a QGridLayout:
With this simple setup, all three plots would be arranged by the QLayout, but they were all independent. This example could be part of a data fitting application, where the main plot shows data and a fit curve. A plot below that will display the residulas (errors) of the fit. Now if a user zooms one of the plots, he would expect that athe x-axes of the two plots are synchronized. The same for a third plot on the rhs of the residuals, which will show a residual histogram. This linking of the axes can be achieved by the following code:
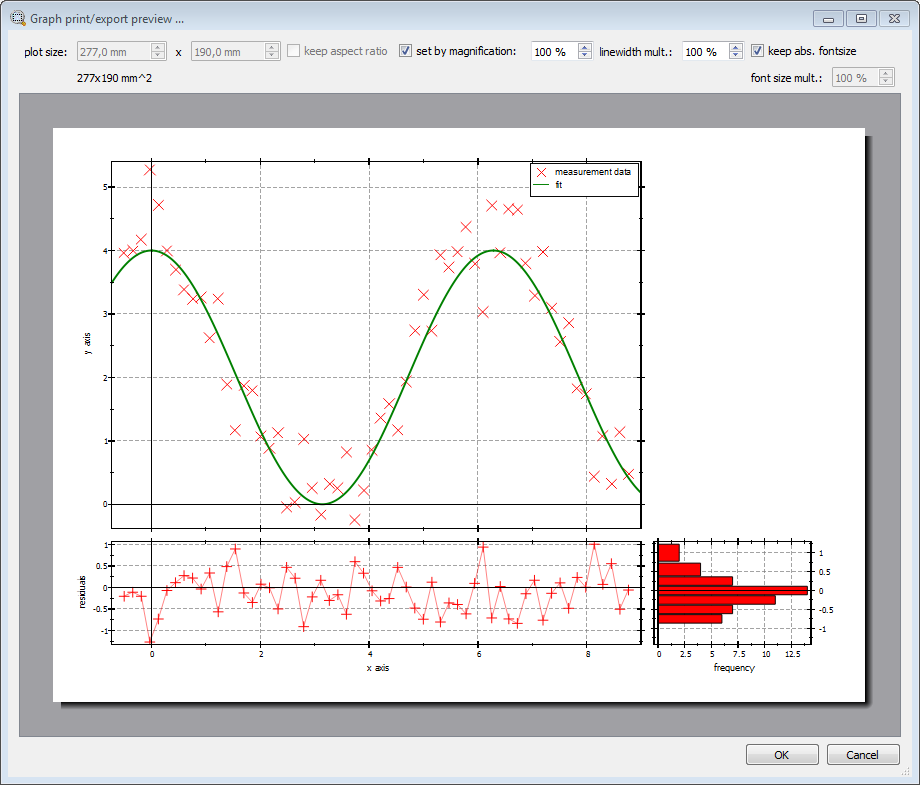
Finally: When printing or saving an image of the plots, the plotter will no know anything about the arrangement of the plots and the plots cannot be printed/drawn in the same arrangement as in the window. If you want to arrange the plots in the same layout in a printout, as in the window, you will have to tell the main plot, in which arrangement to print the plots:
In the first line, grid-printing (i.e. the layouted printing of several graphs) is activated. Then the arrangement of the two slave plots plotResid and plotResidHist is defined as (x,y)-shifts with respect to the master plot plotMain.
Now some data is generated and several curves are added to the graphs. See test_multiplot.cpp for the full source code.
Finally the axes and plots need a bit of formatting to make them look nicer:
As a last step, the axes are scaled automatically, so the data fills the plots:
The result looks like this:
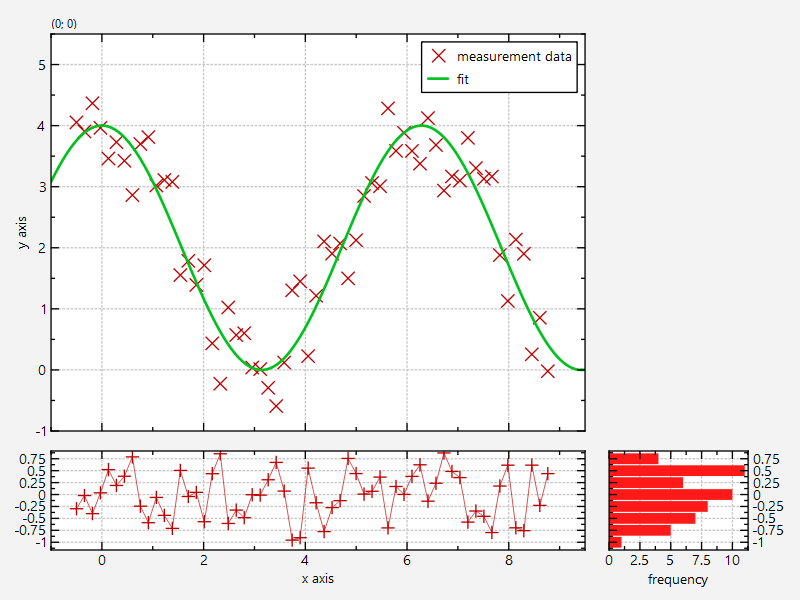
You push the print button ( ) to open a print preview dialog, which will give an impression of how the three plots will be arranged in a printout:
) to open a print preview dialog, which will give an impression of how the three plots will be arranged in a printout:
In addition this example also contains a Window that allows to control the plot layout and synchronization options: