 |
JKQTPlotter trunk/v5.0.0
an extensive Qt5+Qt6 Plotter framework (including a feature-richt plotter widget, a speed-optimized, but limited variant and a LaTeX equation renderer!), written fully in C/C++ and without external dependencies
|
 |
JKQTPlotter trunk/v5.0.0
an extensive Qt5+Qt6 Plotter framework (including a feature-richt plotter widget, a speed-optimized, but limited variant and a LaTeX equation renderer!), written fully in C/C++ and without external dependencies
|
This project (see ./examples/rgbimageplot_cimg/) simply creates a JKQTPlotter widget (as a new window) and shows an RGB image read from a BMP-file. The image is generated as an cimg cimg_library::CImg<uint8_t> image and then copied into a single column of the internal datastore (JKQTPMathImage could be directly used without the internal datastore). To copy the data a special cimg Interface function JKQTPCopyCImgToColumn() is used, that copies the data from a CImg cimg_library::CImg<uint8_t> directly into a column.
The function JKQTPCopyCImgToColumn() is available from the (non-default) header-only extension from jkqtplotter/jkqtpinterfacecimg.h. This header provides facilities to interface JKQTPlotter with cimg. The cimg-binding itself is header-only, and NOT compiled into the JKQtPlotter libraries. Therefore you can simply include the header and use the facilities provided by it.
The CMake-build system of JKQtPlotter (and its examples) provides facilities to allow for find_package(CImg) to compile against that library. If you want to build the CImg-based JKQtPlotter examples (see list above), you either have to ensure that CMake finds CImg by itself (i.e. somewhere in the default search paths, e.g. CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX), or you can set the CMake variable CImg_DIR so it points to the directory of the CImg.h file, or before configuring JKQtPlotter.
The source code of the main application is (see rgbimageplot_cimg.cpp:
The result looks like this:
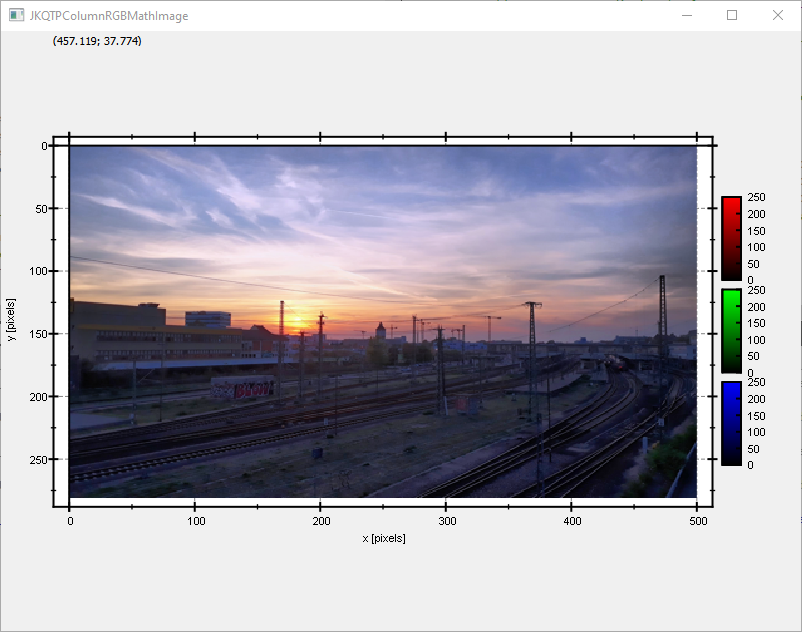
Note the step
above, which ensures that the image is not draw upside-down! This will reorient the y-axis to point from top to bottom (for increasing positive coordinates). The image would be upside-down, because computer images use a coordinate system with 0 at the top-left (left-handed coordinate system) and the JKQTPlotter has its 0 at the bottom-left (right-handed coordinate system).
See examples/rgbimageplot for a detailed description of the other possibilities that the class JKQTPColumnRGBMathImage offer with respect to determining how an image is plotted.