 |
JKQTPlotter trunk/v5.0.0
an extensive Qt5+Qt6 Plotter framework (including a feature-richt plotter widget, a speed-optimized, but limited variant and a LaTeX equation renderer!), written fully in C/C++ and without external dependencies
|
 |
JKQTPlotter trunk/v5.0.0
an extensive Qt5+Qt6 Plotter framework (including a feature-richt plotter widget, a speed-optimized, but limited variant and a LaTeX equation renderer!), written fully in C/C++ and without external dependencies
|
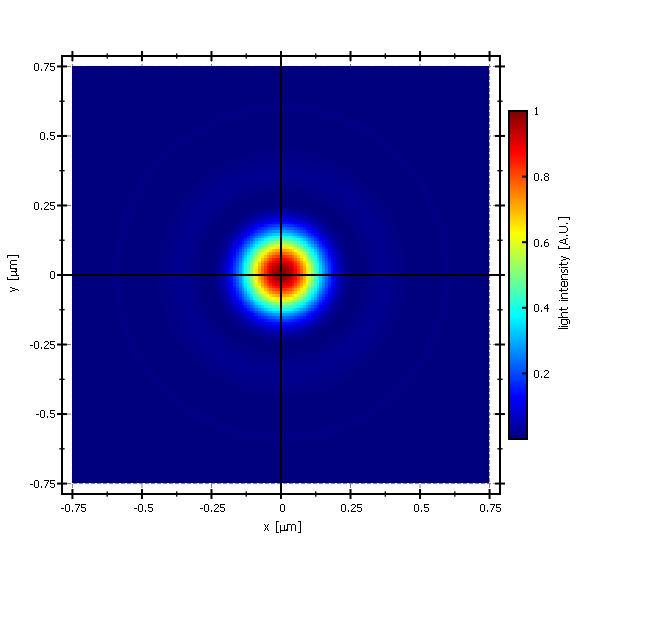
This project (see ./examples/imageplot_opencv/) simply creates a JKQTPlotter widget (as a new window) and adds a color-coded image plot of a mathematical function (here the Airy disk). The image is generated as an OpenCV cv::Mat (see https://opencv.org/) image and then copied into a single column of the internal datastore (JKQTPMathImage could be directly used without the internal datastore). To copy the data a special OpenCV Interface function JKQTPCopyCvMatToColumn() is used, that copies the data from a cv::Mat directly into a column.
The function JKQTPCopyCvMatToColumn() is available from the (non-default) header-only extension from jkqtplotter/jkqtpinterfaceopencv.h. This header provides facilities to interface JKQTPlotter with OpenCV. The OpenCV-binding itself is header-only, and NOT compiled into the JKQtPlotter libraries. Therefore you can simply include the header and use the facilities provided by it.
The CMake-build system of JKQtPlotter (and its examples) is compatible with both OpenCV 3.4.x and 4.x and uses the standard find_package(OpenCV) facilities provided by OpenCV to compile and bind against that library. If you want to build the OpenCV-based JKQtPlotter examples (see list above), you either have to ensure that CMake finds OpenCV by itself (i.e. somewhere in the default search paths), or you can set the CMake variable OpenCV_DIR so it points to the OpenCV directory before configuring JKQtPlotter.
The source code of the main application is (see imageplot_opencv.cpp:
The result looks like this:
See examples/imageplot for a detailed description of the other possibilities that the class JKQTPColumnMathImage (and also JKQTPMathImage) offer with respect to determining how an image is plottet.