|
JKQTPlotter trunk/v5.0.0
an extensive Qt5+Qt6 Plotter framework (including a feature-richt plotter widget, a speed-optimized, but limited variant and a LaTeX equation renderer!), written fully in C/C++ and without external dependencies
|
 |
JKQTPlotter trunk/v5.0.0
an extensive Qt5+Qt6 Plotter framework (including a feature-richt plotter widget, a speed-optimized, but limited variant and a LaTeX equation renderer!), written fully in C/C++ and without external dependencies
|
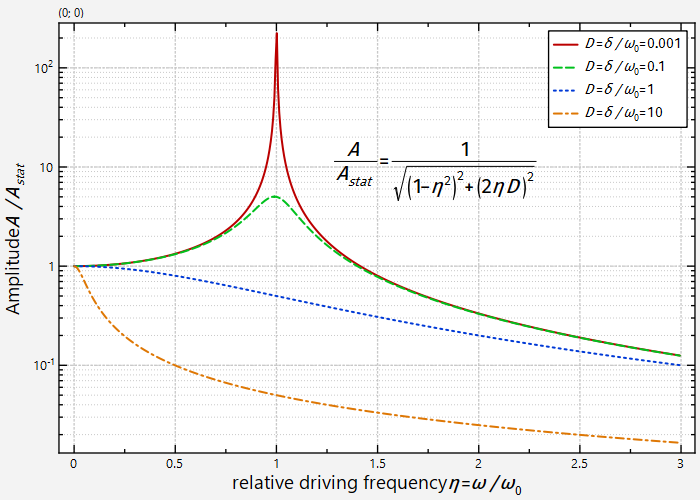
This project (see ./examples/logaxes/) simply creates a JKQTPlotter widget (as a new window) and several line-graphs of different resonance curves.
The source code of the main application can be found in logaxes.cpp. Mainly several graphs are generated in a loop and then different line styles are applied to the graphs (set by `graph->setLineStyle()). The colors are set automtically from an internal default palette. The main loop looks like this:
Then a JKQTPGeoText is added to the graph, which shows the function plotted in the plot:
The difference between not using and using $...$ for the equation can be seen here:
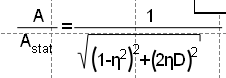
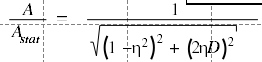
Finally the y-axis is switched to logarithmic scaling and the axis labels are set:
As an alternative JKQTPCALTexponentCharacter does not use the power-of-10 notation, but uses the usual unit-characters, e.g. 0.001=1m, 0.000001=1µ, 10000=10k, ...
The result looks like this:
Without the logarithmic scaling we would have:
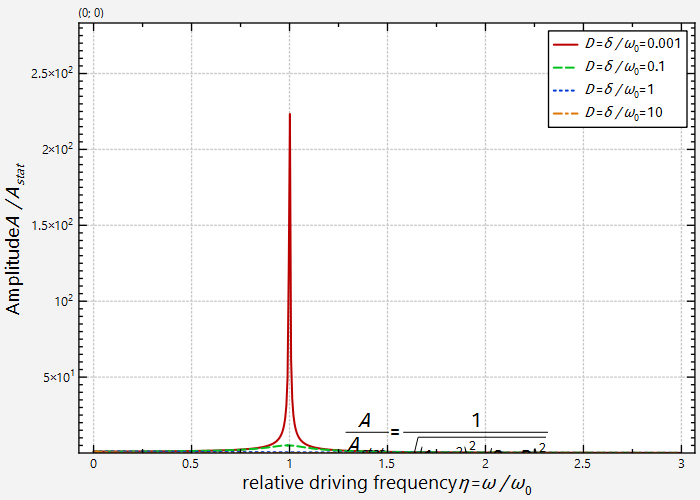
Switching the minor grid off results in a plot like this:
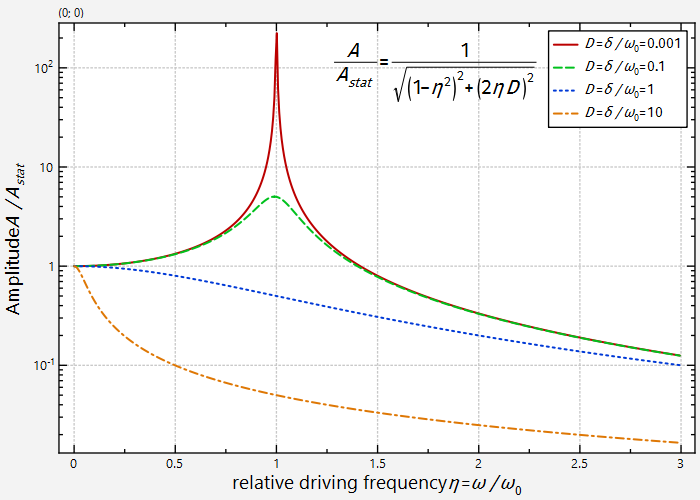
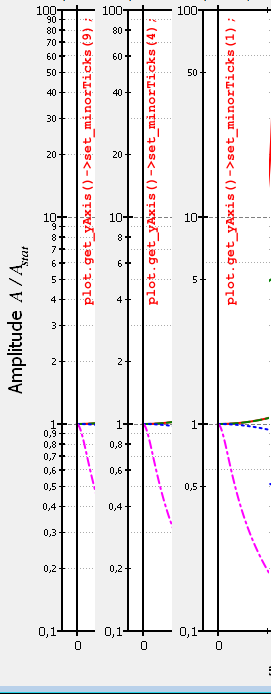
These examples show the results for different typical values for setMinorTicks():
These examples show the results for different typical values for setLabelType():